The challenge of preserving biodiversity looms large, demanding our urgent attention. From the intricate tapestry of life that sustains our planet to the myriad of species that enrich our existence, the loss of biodiversity poses a profound threat to both human well-being and the health of our ecosystems.
This comprehensive guide delves into the complexities of biodiversity conservation, exploring the challenges we face, the strategies we can employ, and the ethical considerations that guide our actions. Through a nuanced examination of habitat loss, invasive species, climate change, and human-wildlife conflict, we illuminate the urgent need to protect and restore the natural world upon which we all depend.
Challenges in Identifying and Monitoring Biodiversity

Identifying and classifying species is a complex task that requires expertise in taxonomy and morphology. Traditional monitoring methods, such as surveys and field observations, are often time-consuming and resource-intensive, and may not provide accurate estimates of biodiversity.
Technological advancements, such as DNA barcoding and remote sensing, offer new opportunities for rapid and cost-effective biodiversity monitoring.
Limitations of Traditional Monitoring Methods
- Subjectivity and observer bias
- Limited spatial and temporal coverage
- Inability to detect cryptic species
Habitat Loss and Degradation
Habitat loss and degradation are major threats to biodiversity. The primary causes include urbanization, deforestation, agriculture, and pollution.
Impacts of Habitat Loss on Biodiversity
- Loss of habitat for species
- Fragmentation of habitats
- Increased vulnerability to extinction
Examples of Successful Habitat Restoration Projects
- Restoration of the Atlantic Forest in Brazil
- Reforestation of the Great Green Wall in Africa
- Restoration of coral reefs in the Maldives
Invasive Species: The Challenge Of Preserving Biodiversity
Invasive species are non-native species that have been introduced to an ecosystem and have become a threat to native biodiversity.
Challenges of Controlling and Managing Invasive Species
- Lack of natural predators or competitors
- High reproductive rates
- Ability to adapt to new environments
Case Studies of Successful Invasive Species Eradication Programs
- Eradication of the cane toad in Australia
- Control of the Asian tiger mosquito in Europe
- Eradication of the American mink in the UK
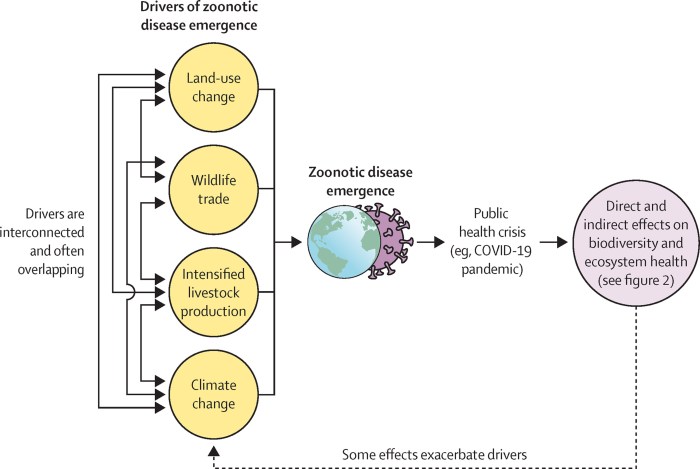
Climate Change

Climate change poses significant threats to biodiversity through direct and indirect effects.
Potential Impacts of Climate Change on Ecosystem Services
- Reduced availability of water
- Loss of habitat
- Changes in species distribution
Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies for Biodiversity Conservation, The challenge of preserving biodiversity
- Establishing protected areas
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions
- Promoting sustainable land management practices
Essential FAQs
What are the primary causes of biodiversity loss?
Habitat destruction, invasive species, climate change, and overexploitation are among the major drivers of biodiversity loss.
How can we effectively monitor biodiversity?
Technological advancements, such as remote sensing and DNA barcoding, enhance our ability to monitor and assess biodiversity.
What role does public awareness play in biodiversity conservation?
Educating the public about the importance of biodiversity and fostering a sense of stewardship are crucial for long-term conservation success.