Fundamental financial accounting concepts 11th edition – Welcome to the realm of financial accounting, where fundamental principles and practices converge to provide a clear understanding of an organization’s financial health. In this 11th edition of Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts, we embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of recording, analyzing, and interpreting financial information.
As we delve into the core concepts of financial accounting, we will explore the accounting equation and its components, unravel the significance of the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows, and gain insights into the process of recording transactions and preparing financial statements.
Core Concepts of Financial Accounting
Financial accounting is the process of recording, classifying, summarizing, and reporting financial information to users both inside and outside an organization.
The fundamental principles of financial accounting include:
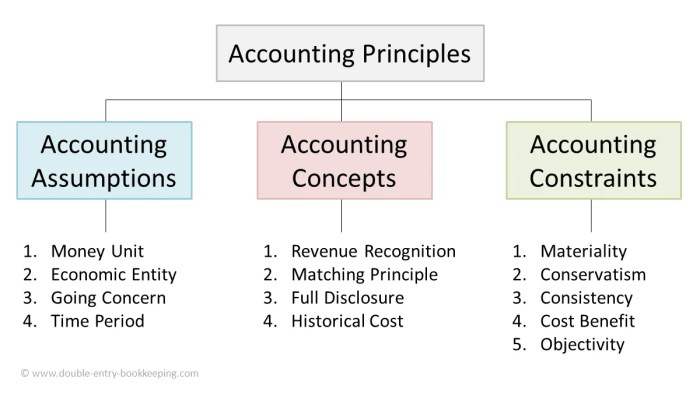
- Objectivity: Financial statements should be prepared without bias or prejudice.
- Materiality: Only information that is material to the financial statements should be disclosed.
- Consistency: Financial statements should be prepared using the same accounting principles and methods from period to period.
- Going concern: The assumption that the entity will continue to operate in the foreseeable future.
The accounting equation is the foundation of financial accounting. It states that Assets = Liabilities + Owners’ Equity.
The balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows are the three main financial statements.
- The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time.
- The income statement shows a company’s revenues and expenses over a period of time.
- The statement of cash flows shows how a company’s cash has changed over a period of time.
Recording Transactions and Preparing Financial Statements
Transactions are recorded in a journal, which is a chronological record of all business transactions.
Journal entries are then posted to ledger accounts, which are individual accounts that track specific assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses.
A trial balance is a list of all ledger accounts and their balances at a specific point in time.
Adjusting entries are made at the end of an accounting period to update the balances of ledger accounts.
Financial statements are prepared after adjusting entries have been made.
Completing the Accounting Cycle

The accounting cycle is the process of recording, classifying, summarizing, and reporting financial information.
The steps involved in closing the books at the end of an accounting period include:
- Preparing a trial balance.
- Making adjusting entries.
- Preparing an adjusted trial balance.
- Closing the income statement accounts.
- Closing the balance sheet accounts.
Financial statements are prepared after closing entries have been made.
Accounting for Assets and Liabilities: Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts 11th Edition
Assets are resources that a company owns or controls.
- Current assets are assets that can be converted into cash within one year.
- Non-current assets are assets that cannot be converted into cash within one year.
Liabilities are debts that a company owes.
- Current liabilities are debts that are due within one year.
- Non-current liabilities are debts that are due more than one year from now.
Accounting for Owners’ Equity

Owners’ equity is the residual interest in the assets of a company after deducting its liabilities.
- Contributed capital is the amount of money that owners have invested in a company.
- Retained earnings are the profits that a company has accumulated over time.
Owners’ equity can be increased by profits and decreased by losses.
Accounting for Revenue and Expenses
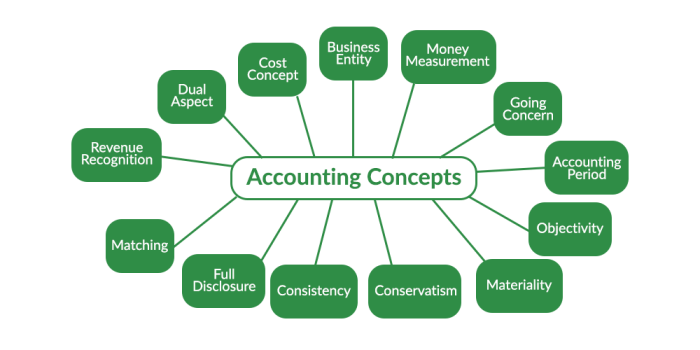
Revenue is the income that a company earns from its operations.
Expenses are the costs that a company incurs in order to generate revenue.
The matching principle states that expenses should be matched to the revenue that they generate.
Special Accounting Topics
Special accounting topics include:
- Accounting for long-term assets and investments
- Accounting for leases and contingencies
- Accounting for changes in accounting estimates
Ethics and Professional Responsibilities in Accounting
Accountants have a responsibility to act in an ethical manner.
The AICPA Code of Professional Conduct provides guidance to accountants on how to act ethically.
Accountants should avoid conflicts of interest and should not engage in any conduct that could damage the reputation of the accounting profession.
FAQ Explained
What are the fundamental principles of financial accounting?
The fundamental principles of financial accounting include accrual accounting, the going concern assumption, the matching principle, and the materiality concept.
What is the purpose of the accounting equation?
The accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Owners’ Equity) provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time.
What are the main components of a balance sheet?
The main components of a balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity.
What is the difference between revenue and expenses?
Revenue is the income generated from the sale of goods or services, while expenses are the costs incurred in generating that revenue.
What are the ethical responsibilities of accountants?
Accountants have a responsibility to maintain confidentiality, avoid conflicts of interest, and act with integrity and objectivity.