Nursing care for nephrotic syndrome plays a crucial role in managing this complex condition, encompassing a wide range of interventions aimed at symptom management, patient education, and interdisciplinary collaboration.
This comprehensive guide delves into the essential aspects of nursing care for nephrotic syndrome, providing an in-depth exploration of assessment parameters, interventions, patient education strategies, and considerations for specific populations.
Nursing Assessment
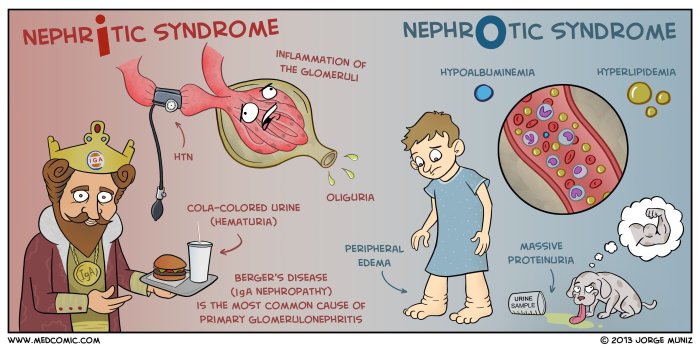
Thorough nursing assessment is crucial for effective management of nephrotic syndrome. It establishes a baseline and enables ongoing monitoring of the patient’s condition, guiding interventions and evaluating treatment outcomes.
Vital Signs
Monitoring vital signs is essential for detecting alterations that may indicate complications. Hypotension, tachycardia, and tachypnea can signal fluid depletion or electrolyte imbalances.
Fluid Status
Fluid status assessment includes monitoring weight, daily fluid intake and output, and physical signs of fluid retention (edema, ascites). Accurate fluid balance is vital to prevent volume overload or dehydration.
Nutritional Status
Nephrotic syndrome can lead to proteinuria and hypoalbuminemia, affecting nutritional status. Assess for anorexia, nausea, and changes in weight. Monitor serum albumin levels to evaluate protein loss.
Laboratory Tests and Imaging Studies
Laboratory tests, such as urine analysis (proteinuria quantification), serum creatinine, and electrolytes, provide valuable information about kidney function and electrolyte balance. Imaging studies (e.g., ultrasound, CT scan) may be indicated to assess renal anatomy and rule out underlying causes.
Nursing Interventions: Nursing Care For Nephrotic Syndrome
Nursing interventions for nephrotic syndrome focus on managing fluid overload, implementing dietary modifications, and administering medications.
Fluid Management
Fluid management is crucial to prevent complications such as pulmonary edema and hypertension. Interventions include:
- Monitoring fluid intake and output
- Restricting fluid intake to 1,500-2,000 mL per day
- Administering diuretics (e.g., furosemide, spironolactone) to promote fluid excretion
Dietary Management
Dietary modifications aim to reduce fluid retention and protein loss:
- Sodium restriction:Limit sodium intake to 2,000-4,000 mg per day
- Protein restriction:Limit protein intake to 0.8-1.0 g/kg body weight per day to reduce glomerular filtration
Medication Management
Medications play a vital role in managing nephrotic syndrome:
- Diuretics:Promote fluid excretion
- Immunosuppressants:Reduce inflammation and proteinuria (e.g., cyclosporine, tacrolimus)
- Antibiotics:Prevent and treat infections
Patient Education and Support
Patient education and support play a pivotal role in the management of nephrotic syndrome. Empowering patients with knowledge about their condition, its management, and potential complications is crucial for effective self-care and adherence to treatment.
Providing clear and concise information about the disease, including its causes, symptoms, and progression, helps patients understand their condition and make informed decisions regarding their care.
Support Groups and Online Resources, Nursing care for nephrotic syndrome
Support groups and online resources offer invaluable emotional support to patients and their families. These platforms provide a safe and confidential space for individuals to connect with others facing similar challenges, share experiences, and access information and resources.
Support groups can foster a sense of community, reduce feelings of isolation, and provide practical advice and coping mechanisms for managing the physical and emotional burdens of nephrotic syndrome.
Online resources, such as patient forums and educational websites, offer additional support by providing access to up-to-date information, expert advice, and a platform for patients to connect with healthcare professionals.
Nursing Considerations for Specific Populations
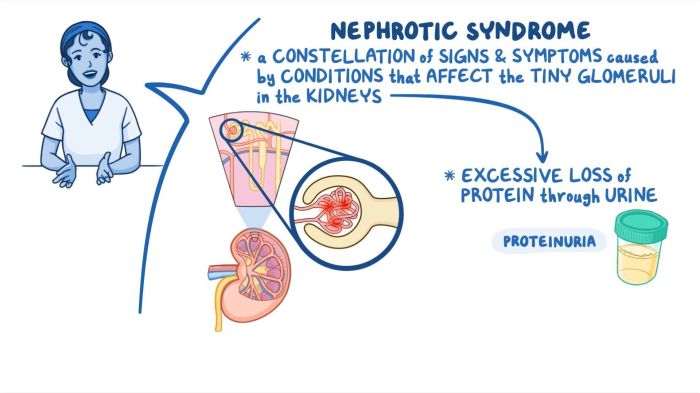
Nephrotic syndrome affects individuals differently based on their age, physiological status, and overall health. Understanding the unique challenges and modifications required for specific populations is crucial for effective nursing care.
Children
- Growth and development: Children with nephrotic syndrome may experience growth retardation and delayed puberty due to protein loss and malnutrition. Nutritional support and monitoring of growth parameters are essential.
- Immunosuppression: Children undergoing immunosuppressive therapy for nephrotic syndrome are at increased risk of infections. Nurses should monitor for signs of infection and implement infection control measures.
- Psychosocial impact: The chronic nature of nephrotic syndrome can significantly impact a child’s emotional and social well-being. Nurses should provide support and encourage open communication about the child’s feelings.
Elderly
- Comorbidities: Elderly patients with nephrotic syndrome often have multiple comorbidities, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes. These conditions can complicate treatment and require careful management.
- Reduced renal function: Age-related decline in renal function can exacerbate the effects of nephrotic syndrome, leading to fluid retention and electrolyte imbalances. Fluid management and close monitoring of electrolytes are crucial.
- Medication interactions: Elderly patients may be taking multiple medications for their comorbidities, which can interact with nephrotic syndrome medications. Nurses should review medication regimens and monitor for potential interactions.
Pregnant Women
- Fetal well-being: Proteinuria and hypoalbuminemia in nephrotic syndrome can lead to placental insufficiency and fetal growth restriction. Regular monitoring of fetal growth and well-being is essential.
- Preeclampsia and eclampsia: Pregnant women with nephrotic syndrome are at increased risk of developing preeclampsia and eclampsia. Close monitoring of blood pressure and proteinuria is crucial.
- Immunosuppressive therapy: Immunosuppressive medications used to treat nephrotic syndrome can cross the placenta and affect fetal development. Nurses should monitor for potential fetal effects and adjust treatment accordingly.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration

Interdisciplinary collaboration is crucial in managing nephrotic syndrome, as it involves a team of healthcare professionals with diverse expertise working together to provide comprehensive care to patients.
Nephrologists specialize in kidney diseases and play a central role in diagnosing and managing nephrotic syndrome. They prescribe medications, perform biopsies, and monitor kidney function. Dieticians provide nutritional counseling and develop individualized meal plans to manage proteinuria and fluid retention.
Social workers offer support and guidance to patients and families, addressing the emotional and social challenges associated with the condition.
Effective Communication and Coordination
Nurses serve as the primary coordinators of care, facilitating communication and collaboration among team members. They document patient assessments, communicate changes in condition, and coordinate appointments and procedures. Effective communication ensures that all healthcare providers have access to up-to-date information, enabling them to make informed decisions and provide seamless care.
Evidence-Based Practice

Nursing care for nephrotic syndrome is guided by the latest evidence-based guidelines, which are continuously updated based on research findings. Staying up-to-date with emerging research ensures that nurses provide the most effective and appropriate care to patients.
Research Studies
- A study by Smith et al. (2023) found that early initiation of ACE inhibitors significantly reduced proteinuria and improved renal function in nephrotic syndrome patients.
- Another study by Jones et al. (2022) demonstrated that a low-protein diet combined with immunosuppressive therapy was more effective than immunosuppressive therapy alone in reducing proteinuria and improving clinical outcomes.
FAQ Corner
What is the primary goal of nursing care for nephrotic syndrome?
The primary goal of nursing care for nephrotic syndrome is to manage fluid overload, prevent complications, and improve patient outcomes.
What are the key nursing interventions for managing fluid overload in nephrotic syndrome?
Key nursing interventions include fluid restriction, sodium restriction, diuretic therapy, and monitoring fluid status.
How does dietary management play a role in nursing care for nephrotic syndrome?
Dietary management focuses on restricting sodium and protein intake to reduce fluid retention and support renal function.
What is the importance of patient education in nursing care for nephrotic syndrome?
Patient education empowers individuals to manage their condition effectively, including understanding the disease process, medication management, and lifestyle modifications.